Introductory Psychology Open Course: Unit 10
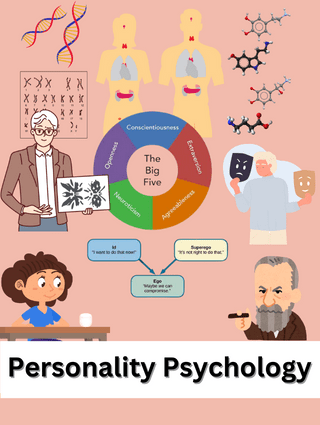
Personality Psychology
In addition to differences in cognitive abilities, which we looked at in the previous unit, people also differ in their personality traits and their characteristic patterns of thinking and behaving. In this unit we'll consider how we can categorize and interpret the ways that people differ in their traits and how these relate to their ways of perceiving and acting in the world.

What do we mean by personality?

Freudian Personality Structure: the Id, Ego, & Superego

Freud's Psychosexual Stages of Personality Development

Freudian defense mechanisms for managing anxiety

Other Psychdynamic theorists: Adler, Horney, & Jung

The projective approach for assessing personality

The trait-based approach for assessing personality

The Forer Effect in assessing accuracy

The MMPI for assessing personality

Considering the relative importance of traits for behavior

Costa & McCrae's Five-Factor model of personality traits

How well do trait scores predict actual behavior?

What might cause differences in personality?

How do genes relate to personality?

The socio-cognitive approach to personality

How meaning & knowledge of death may influence personality

The humanistic approach & drives to improve

How views of ourselves & our abilities influence personality

How views of ourselves & our abilities influence personality

The flaws of the popular Myers-Briggs Type Indicator

Additional Resources: